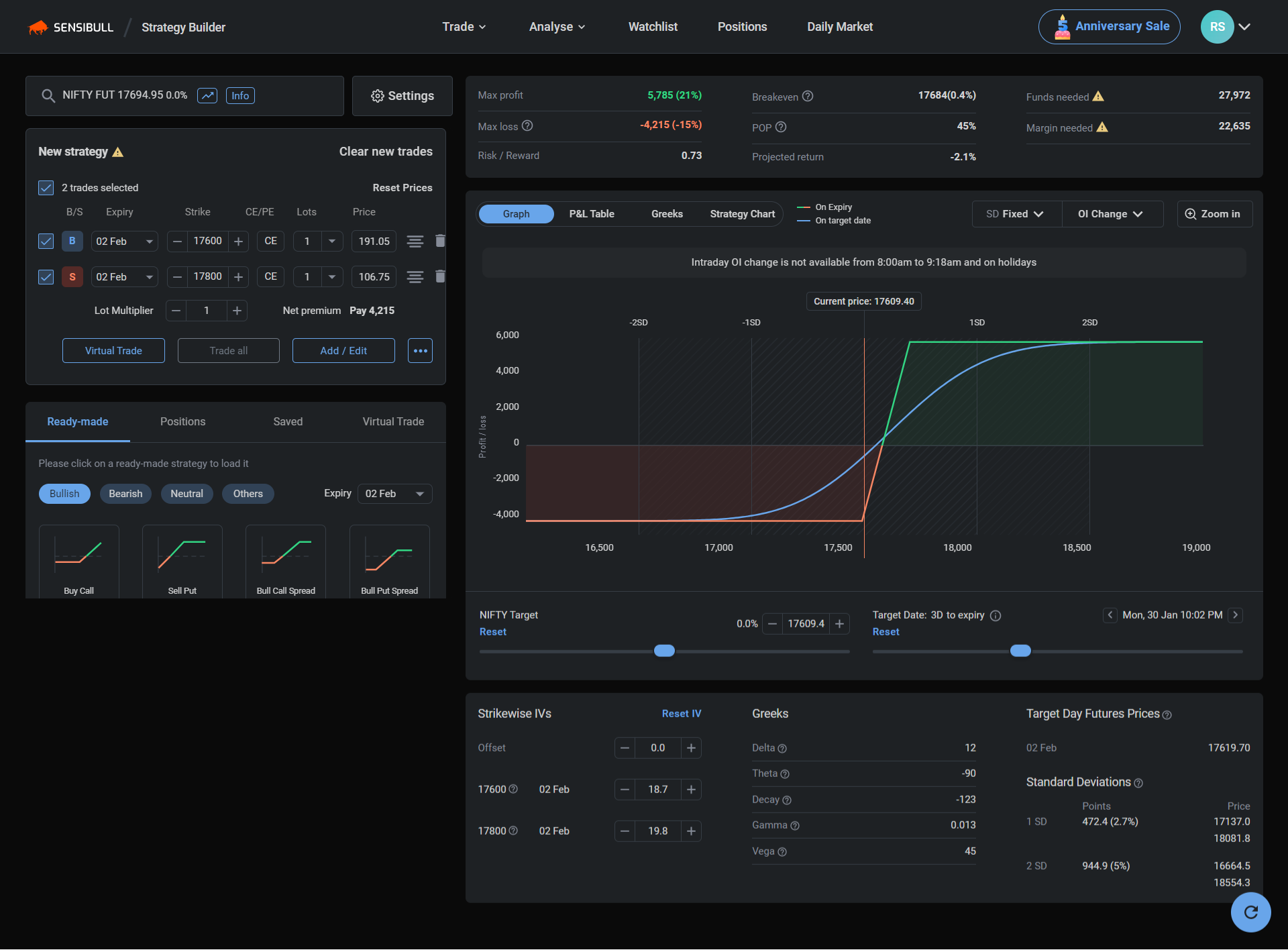
Bull Put Spread is an options trading strategy that involves simultaneously selling a put option at a specific strike price and buying another put option at a lower strike price. The goal of this strategy is to generate income through the sale of the higher strike price put option, while also limiting the potential loss if the underlying asset's price increases.
The Bull Put Spread strategy is a limited risk strategy because the most you can lose is the difference between the strike prices of the options sold and bought, minus the premium received. The profit potential is also limited, as the most you can make is the premium received.
Table of Contents
how to apply a Bull Put Spread strategy
-
Identify the underlying asset: Select the underlying asset you wish to trade, such as a stock, index, or commodity.
-
Set the strike prices: Choose two strike prices for the options you will sell and buy. The higher strike price should be at the current market price or slightly above it. The lower strike price should be set at a price where you expect the underlying asset to be by the expiration date.
-
Sell the options: Sell one put option at the higher strike price.
-
Buy options: Buy one put option at the lower strike price.
-
Monitor the trade: Keep an eye on the underlying asset's price, and the option's prices and volatility. Adjust the trade if necessary by buying or selling additional options as required.
-
Expiration: Close the trade or let it expire on the expiration date. If the underlying asset's price is above the higher strike price you set, you can make a profit.
It's important to note that this is just an example and that options trading can be quite complex and require significant knowledge and experience. Additionally, It's important to consider the risks involved in any trading strategy and to use proper risk management techniques. It's also worth to mention that the Bull Put Spread strategy is generally used when the market is expected to increase or at least not to make a large move in the downside direction.






